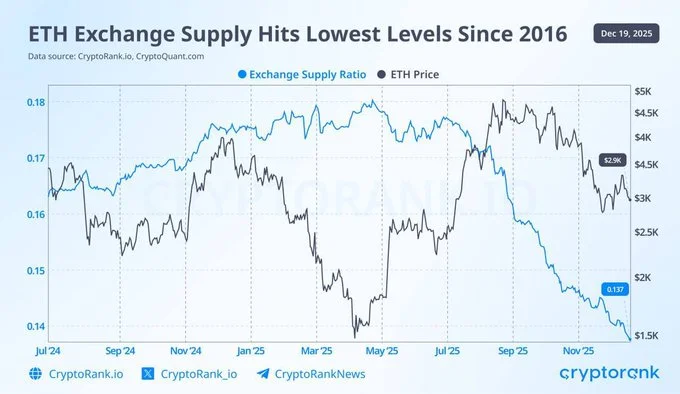
Ethereum is experiencing one of its most significant supply contractions in nearly a decade. Data from on-chain analytics platforms shows that the amount of ETH held on centralized exchanges has fallen to its lowest point since 2016, a period when Ethereum was still in its early growth phase.
The decline points to reduced short-term sell pressure as more holders move ETH into long-term storage, staking contracts, and institutional treasuries.
According to CryptoQuant, Ethereum’s exchange balance ratio has dropped to approximately 0.137, underscoring how much of the circulating supply is now sitting off exchanges. This shift reflects growing caution among traders and rising conviction among long-term holders who appear increasingly unwilling to sell at current prices.
“Ethereum’s exchange supply has fallen to levels not seen since 2016, signaling a significant tightening in the available ETH for trading.”
Structural Supply Shift Driven by Staking and Institutions

A major contributor to this supply squeeze is Ethereum’s staking ecosystem. More than 37 million ETH is now locked in staking, effectively removing a large portion of supply from active circulation. Staked ETH cannot be sold instantly, which limits immediate liquidity and amplifies price sensitivity when demand increases.
At the same time, institutional and corporate accumulation has accelerated. Public data shows that 27 public entities now collectively hold an estimated $17.7 billion worth of ETH, equivalent to roughly 5.96 million ETH. These holdings are typically long-term strategic positions rather than short-term trades, further reducing sell-side pressure.
“Over 37 million ETH is locked in staking, while 27 public entities hold $17.7 billion in ETH, signaling a structural shift in Ethereum’s supply dynamics.”
One of the most notable recent accumulations came from BitMine Immersion, which reportedly added more than 400,000 ETH to its balance in the last 30 days. Moves of this scale highlight how corporate treasuries are increasingly viewing ETH as a long-term asset rather than a speculative trade.
Liquidity Tightening Raises Volatility Risk
While shrinking exchange balances often support price appreciation, they can also increase volatility. With less ETH readily available for trading, even modest changes in demand can lead to sharper price movements in either direction.
This dynamic has appeared in previous market cycles, where similar supply contractions were followed by explosive rallies once demand picked up.
Historical data suggests that Ethereum’s past exchange supply drawdowns often preceded strong upside moves, especially when accompanied by rising institutional participation. Analysts note that today’s environment differs from earlier cycles, as staking, ETFs, and corporate holdings now play a much larger role in shaping supply behavior.
Layer-2 networks such as Base and Arbitrum are also absorbing ETH liquidity. As ETH is bridged and locked into scaling solutions, it becomes less accessible for spot trading, reinforcing the broader trend of declining liquid supply.
Market Structure and Technical Outlook
As of December 2025, Ethereum is consolidating around the $3,090 level. Despite short-term volatility, the broader market structure remains intact, with ETH still forming higher lows compared to its 2022 cycle bottom. Trading volume has remained robust, hovering around $11.5 billion, suggesting that market participation remains strong even as liquid supply tightens.
Technical indicators present a mixed picture. Momentum signals such as the MACD and RSI point to ongoing consolidation, while price action shows ETH trading below some key daily moving averages.
A sustained move above the $3,000–$3,100 range could strengthen the short-term outlook, while holding former resistance near the $3,800–$4,000 zone would reinforce the longer-term uptrend.
Some analysts continue to project higher price targets based on historical impulse patterns, arguing that reduced supply combined with renewed demand could push ETH significantly higher over time.
What the Supply Squeeze Means Going Forward
Ethereum’s declining exchange supply reflects more than just short-term market behavior. It signals a deeper transformation in how ETH is held and used. With over 30% of total supply staked and a growing share locked in institutional treasuries, Ethereum is becoming structurally less liquid than in previous cycles.
“This surge in institutional accumulation adds a new layer of demand not seen in earlier cycles, reducing the likelihood of sudden sell-offs.”
For investors, this environment creates both opportunity and risk. Lower liquidity can magnify upside during demand surges, but it can also intensify drawdowns if sentiment turns negative. Monitoring institutional flows, ETF activity, and staking trends will be crucial in assessing Ethereum’s next major move.
While short-term technical signals remain mixed, the underlying supply dynamics suggest Ethereum is entering a phase where scarcity, rather than speculation alone, may increasingly drive price action.
No related posts.